This page by David Mark Papkin shows useful network links
Enroll in Cisco Networking Academy
200-301 CCNA Exam Topics Study Tool
Packet Tracer
Packet Tracer is a free network simulator tool for certification exam preparation, particularly for CCNA students. It’s available directly through the Cisco Networking Academy. Download and install the Packet Tracer software by signing up for the Introduction to Packet Tracer course, which teaches you the basics of using the tool.
Cisco Learning Labs offer you a chance to practice lab exercises on a virtual lab topology hosted by Cisco and grouped according to the certification exam for which you’re studying. When you choose an exam, you can purchase the rights to practice lab exercises for topics on that exam. During a three-month access, you can use a virtual lab pod to run real IOS (routers and switches).
Purchase Cisco Learning Labs here
Cisco Modeling Labs is an on-premise network simulation tool that runs on workstations and servers and lets you easily simulate Cisco and non-Cisco networks using real Cisco images. This gives you highly reliable models for designing, testing, and troubleshooting. Compared to building out real-world labs, Cisco Modeling Labs returns results faster, more easily, and for a fraction of the cost.
Purchase Cisco Modeling Labs – Personal here
Collaboration Certifications Roadmap Webinar
Shows config and lists different syslog levels
Configuring System Message Logging (Cisco)
Configure System Logging (Cisco link)
Configuring Cisco IOS to automatically save the running configuration to a tftp server on save
Booting Cisco Router from a TFTP server
Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers
Understanding Cisco Auto Archive Feature to Backup Configuration File
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers
Interface and Line Numbers in Cisco Routers
Errdisable Port State Recovery on the Cisco IOS Platforms
Maximum Number of Interfaces and Subinterfaces for Cisco IOS Routers: IDB Limits
Overview of Dial Interfaces, Controllers, and Lines
Access Lists
Standard Access Lists – Filters bases on Source Address and Wildcard mask
Extended Access Lists – Filters based Source Address, Destination Address, Wildcard mask, Protocol and Port.
Ansible
https://developer.cisco.com/learning/labs/ansible-03_ansible-hands-on/ansible-hands-on/
APIPA – Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) was developed by Microsoft as a
means for clients that could not contact a DHCP server to communicate on the
local network anyway. If a Windows host does not receive a response from a DHCP
server within a given time frame, it selects an address at random from the range
169.254.1.1 to 169.254.254.254.
These addresses are from one of the address ranges reserved for private addressing
(169.254.0.0/16). The first and last subnets are supposed to be unused.
This type of addressing is referred to as link local in standards documentation
(RFC 3927).
APIPA has no mechanism for assigning default gateway or DNS server addresses.
Hosts using APIPA are restricted to communicating on the local network
Cabling
WHAT DOES UTP, S/UTP, FTP, STP AND SFTP MEAN?
What is the difference between shielded and unshielded network cables
Cisco Cable Pinouts ( rollover , aux , Ethernet )
ISO/IEC_11801 wiring standards
https://tripplite.eaton.com/products/ethernet-cable-types
| Category | Max. Data Rate | Bandwidth | Max. Distance | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | 1 Mbps | 0.4 MHz | Telephone and modem lines | |
| Category 2 | 4 Mbps | 4 MHz | LocalTalk & Telephone | |
| Category 3 | 10 Mbps | 16 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | 10BaseT Ethernet |
| Category 4 | 16 Mbps | 20 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | Token Ring |
| Category 5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | 100BaseT Ethernet |
| Category 5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | 100BaseT Ethernet, residential homes |
| Category 6 | 1 Gbps | 250 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) 10Gb at 37 m (121 ft.) | Gigabit Ethernet, commercial buildings |
| Category 6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | Gigabit Ethernet in data centers and commercial buildings |
| Category 7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) | 10 Gbps Core Infrastructure |
| Category 7a | 10 Gbps | 1000 MHz | 100 m (328 ft.) 40Gb at 50 m (164 ft.) | 10 Gbps Core Infrastructure |
| Category 8 | 25 Gbps (Cat8.1) 40 Gbps (Cat8.2) | 2000 MHz | 30 m (98 ft.) | 25 Gbps/40 Gbps Core Infrastructurezxccc |
Fiber Optics Part 2: Single-Mode Fiber vs. Multi-Mode-Fiber
Differences between T568A and T568B explained
Power over Ethernet (POE) pinout
https://www.ppc-online.com/blog/fiber-connectors-whats-the-difference
https://www.cablematters.com/Blog/Networking/fiber-optic-connector-types
Cisco Optics-to-Device Compatibility Matrix
How to use a punchdown tool video (very good!!!)
Configuration Monitoring
Configuration management tools can monitor device configurations to discover when the
device configuration differs from the intended ideal configuration, and then either reconfigure the device or notify the network engineering staff to make the change
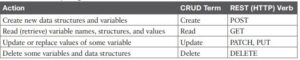
CRUD and HTTP Verbs
The software industry uses a memorable acronym—CRUD—for the four primary actions performed by an application.
Create: Allows the client to create some new instances of variables and data structures at the server and initialize their values as kept at the server
Read: Allows the client to retrieve (read) the current value of variables that exist at the server, storing a copy of the variables, structures, and values at the client
Update: Allows the client to change (update) the value of variables that exist at the server
Delete: Allows the client to delete from the server different instances of data variables
For example, using the northbound REST API of a DNA controller (See Cisco Software-Defined Access (SDA),” for info) you might want to create something, like a new security policy. From a programming perspective, the security policy exists as a related set of configuration settings on the DNA controller, internally represented by variables. To do that, a REST client application would use a Create action, using the DNA Center RESTful API, that created variables on the DNA Controller via the DNA Center REST API.
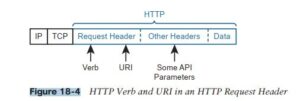
HTTP uses verbs that mirror CRUD actions. HTTP defines the concept of an HTTP request and reply, with the client sending a request and with the server answering back with a reply.
Each request/reply lists an action verb in the HTTP request header, which defines the HTTP action. The HTTP messages also include a URI, which identifies the resource being manipulated for this request. As always, the HTTP message is carried in IP and TCP, with headers and data, as seen below.
DHCP
Cisco IP Addressing: DHCP Configuration Guide
DHCP Static Binding on Cisco IOS
CSMA/CD – Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. It is a network protocol used primarily in early Ethernet networks (especially 10Base-T and 10Base2 Ethernet) to control access to a shared transmission medium (e.g., a coaxial cable or hub-based Ethernet).
Breakdown of CSMA/CD:
1. CS – Carrier Sense
- What it means: Before a device attempts to send data, it listens to (senses) the network to check if another device is already transmitting.
- Purpose: Avoids transmission when the line is already busy.
2. MA – Multiple Access
- What it means: Multiple devices are connected to and share the same communication medium.
- Implication: Any of the devices can try to send data at any time.
3. CD – Collision Detection
- What it means: While transmitting, a device monitors the medium to detect if another device started transmitting at the same time (collision).
- If a collision is detected:
- The devices stop transmitting immediately.
- They wait for a random backoff time before trying again (using exponential backoff).
Where CSMA/CD Is Used:
| Used In | Notes |
|---|---|
| Classic Ethernet (10Base5, 10Base2, 10Base-T with hubs) | Shared medium networks – prone to collisions |
| Half-Duplex Ethernet | Only one direction of traffic at a time; collisions are possible |
| Legacy environments | Mostly obsolete in modern full-duplex switched Ethernet networks |
Where CSMA/CD Is NOT Used:
- Modern switched Ethernet (Full-Duplex): No collisions occur because each device has a dedicated path to the switch.
- Wi-Fi (uses CSMA/CA instead): Collision Avoidance is used due to different characteristics of wireless communication.
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping is a feature that determines which devices attached to switch ports can respond to DHCP requests. DHCP snooping can be used to prevent unauthorised DHCP messages that contain information such as IP address-related data being provided to legitimate network devices.
Enable DHCP Snooping Globally
Router(config)#ip dhcp snooping
Configure DHCP server facing switch port as trusted
Router(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping trust
Configure Snooping rate limit ex: 100 pps
Router(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping rate limit 100
Configure Snooping Database agent
Router(config)# ip dhcp snooping database tftp://10.1.1.1/dir/file
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Test/dwerblo/broken_guide/snoodhcp.html
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
To prevent unauthorized Address Resolution Protocol , use Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
To configure DAI
Step 1. Use the ip arp inspection vlan vlan-list global command to enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) on the switch for the specified VLANs. Step 2. Separate from the DAI configuration, also configure DHCP Snooping and/or ARP ACLs for use by DAI. Step 3. Configure the ip arp inspection trust interface subcommand to override the default setting of not trusted.
Etherchannel
Configuring Link aggregation with Etherchannel
- Increases bandwidth without upgrading equipment
- Adds High Availability
- Acts as 1 link to STP, so that multiple links stay active
- Active / Active Load Balancing
- Scalable
- Most configuration tasks can be done on the EtherChannel interface instead of on each individual port, ensuring configuration consistency throughout the links.
Event Prioritization and Alerting
| Event Prioritization | Alerting | Why It Matters |
|---|
| Determine event importance from devices | Automated alerts based on event severity | Prevents performance issues |
| Categorize events, Emergency (0) to Debug (7) | Triggered by event types, thresholds, or anomalies | Filters out non-critical alerts |
| Identify immediate action vs. informational events | Alerts need attention; notifications inform | Prioritizes critical events for system integrity |
GRE
How to configure GRE over an IPSec tunnel on routers
HTTP Headers – used to pass additional information between the clients and the server through the request and response header. All the headers are case-insensitive, headers fields are separated by colon, key-value pairs in clear-text string format.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/http-headers/
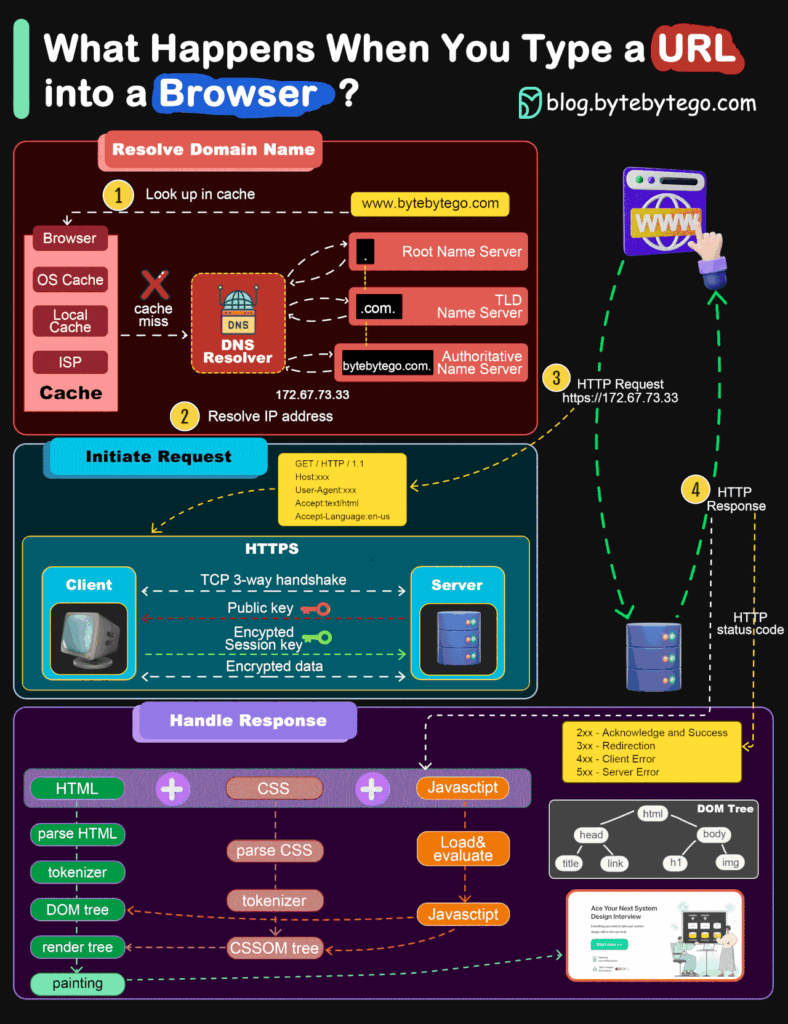
What happens when you type a URL into a browser?
HSRP
Cisco Campus Network for High Availability Design Guide
Cisco What Is Administrative Distance?
Hypervisor
How to Install Linux in VirtualBox
Downloads – Oracle VM VirtualBox
How to Install Apache Server and Set Up Virtual Hosts on Ubuntu 22.04
https://www.wikihow.com/Install-VirtualBox
How to Fix “VT-X Is Not Available (verr_vmx-No-Vmx)” Error in VirtualBox
Install Linux on Windows with WSL
How To Install KVM Hypervisor on Ubuntu 22.04|20.04
MAC Hypervisor
Intent-based Networking
SDN is a foundational building block of intent-based networking. Cisco Catalyst Center provides a single dashboard for managing and controlling the enterprise network.
Tools of Cisco Catalyst Center
- Discovery – Scans the network for new devices.
- Inventory – Provides inventory for new devices.
- Topology – Discover and map new devices to a physical topology.
- Image Repository
- Command Runner
- License Manager
- Template Editor
- Network Plug and Play
- Telemetry
- Data and Reports
IPv4
Configure IP address on Cisco router
Configure Cisco switch settings
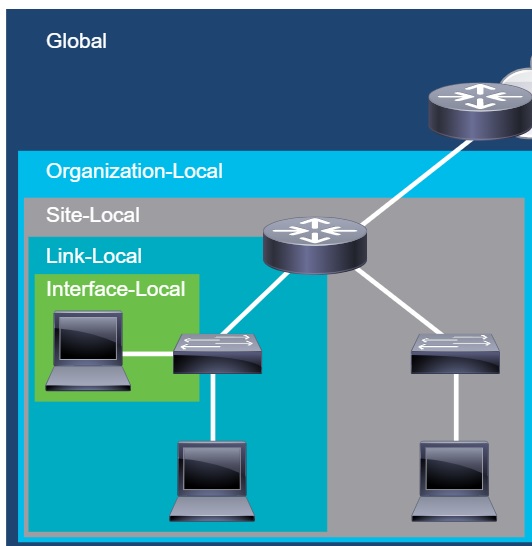
IPv6
IPv6 scope
IP Phones
How to Access the Web Configuration Page of a Cisco IP Phone 6800 Series
Designing an Enterprise IP Telephony Network
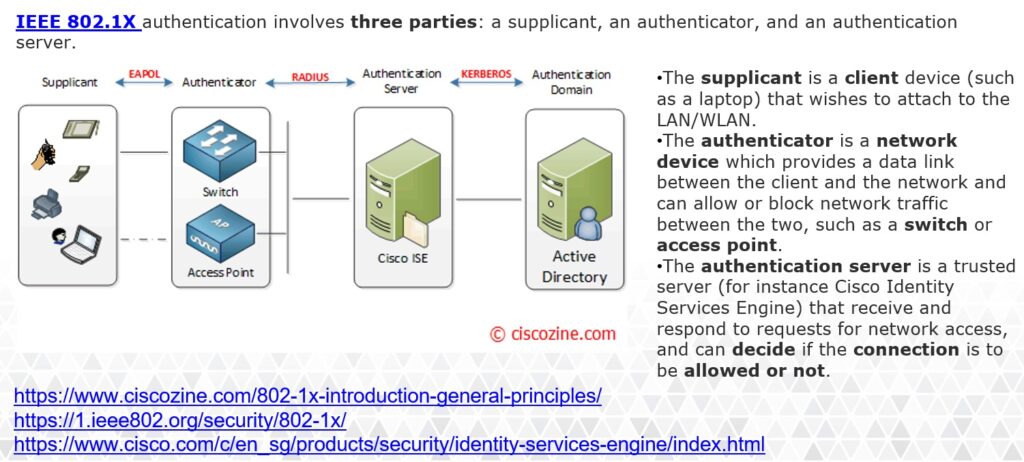
ISE
https://www.routexp.com/2019/05/introduction-to-secure-group-tagging-sgt.html
https://www.securew2.com/blog/eap-tls-vs-eap-ttls-pap
Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
Logging
Logging commands:
Configure syslog
logging host w.x.y.z – Log messages to a syslog server with IP address w.x.y.z
logging trap informational
Log terminal sessions
terminal monitor – Log messages to a non console terminal session during the current session.
show logging – Verify the “terminal monitor” command.
Loopback
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/800M/software/800MSCG/routconf.html#48525
Understanding the Loopback Interface & Loopback Address – Study CCNA (study-ccna.com)
Network Address Translation (NAT)
3 kinds ( Static, Dynamic and Overload )
- Static – 1 to 1 mapping, requires a Public IP for EACH Private IP you want to translate.
- Dynamic – Many to Many mapping, can use a pool of Public IP addresses to translate ANY Private IP mentioned in the access list.
- Overload ( Pat ) – It translates many Private (local)l addresses into a single global address.
Advantages –
- Reuse of private IP addresses
- Enhancing security for private networks by keeping internal addressing private from the external network
- Connecting a large number of hosts to the global Internet using a smaller number of public (external) IP address, thereby conserving IP address space.
Disadvantages –
- No end to end security
- Performance
- Application usage. Since hosts inside the network is unreachable at times, some applications tends to have compatibility issues with NAT. These applications depend on end to end functionality which the network fails to supply.
- Protocol Usage. Since the value inside the headers are changed in NAT, tunneling protocols such as IPSec can be complicated to be used. Whenever the values inside the headers are modified, the integrity checks are interfered causing them to fail.
NAT: Local and Global Definitions
Network Architecture
Three-tier Architecture
- Access layer: Provides workgroup/user access to the network
- Distribution layer: Provides policy-based connectivity and controls the boundary between the access and core layers
- Core layer: Provides fast transport between distribution switches within the enterprise campus
Spine and Leaf Architecture (two-tier)
Spine-and-Leaf Architecture: Design Overview White Paper
Network Diagram tools
Visual Paradigm Online (VP Online) Free Edition
Diagram Designer 1.29.5 FreeWare
Five free apps for diagramming your network
Network Management tools/ NMS
Network Performance Monitor (NPM) Multi-vendor network monitoring that scales and expands with the needs of your network
Paessler Router Traffic Grapher (PRTG) Monitor all the systems, devices, traffic, and applications in your IT infrastructure.
ManageEngine OpManager Monitor routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and VMs for fault and performance
WhatsUp Gold provides complete visibility into the status and performance of applications, network devices and servers in the cloud or on-premises.
Cisco DNA a powerful network controller that resides on a physical appliance, with virtual appliance support to come in the future.
OSPF
Q What two parameters must be configured for basic OSPF to work properly?
A Process ID and Area.
OSPF: Frequently Asked Questions
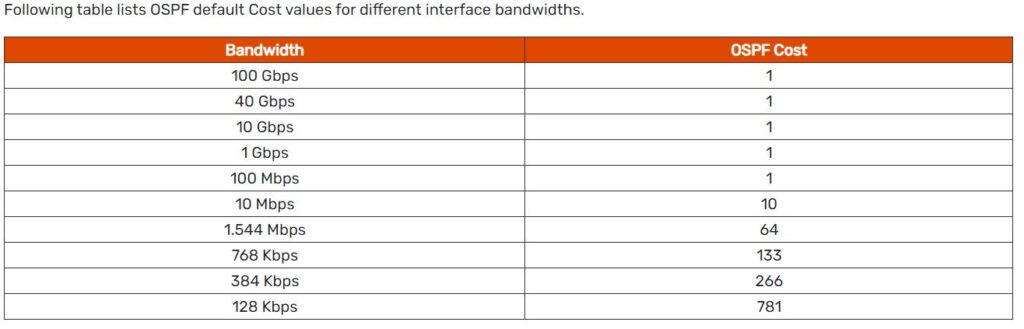
Modifying OSPF cost.
The default reference bandwidth used for calculating cost on CIsco routers is 100Mbps
OSPF uses a simple formula to calculate the OSPF cost for an interface with this formula:
cost = reference bandwidth / interface bandwidth
However, if you have faster links in your network, such as gigabit Ethernet or OC-3 connections, OSPF can’t give these links a better cost than 1. So you should set the reference bandwidth to at least as high as the fastest link in your network. In fact, you may want to set this value higher than the bandwidth of your fastest link to ensure that you don’t have to reconfigure your whole network when you eventually upgrade
https://www.cisco.com/c/m/en_us/techdoc/dc/reference/cli/nxos/commands/ospf/auto-cost-ospf.html
What is OSPF Metric value Cost and OSPF default Cost Reference Bandwidth
Cisco IOS Cookbook, 2nd Edition by Kevin Dooley, Ian Brown
DR/BDR Election
Designated & Backup Designated Router
Configuring Per Interface OSPF
Enabling OSPFv2 on an Interface Basis
Packet Tracer
Password Encryption
QOS
Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration Guide
RADIUS vs TACACS+
| RADIUS | TACACS+ | |
| Protocol and Port(s) Used | UDP: 1812 & 1813 -or- UDP: 1645 & 1646 | TCP: 49 |
| Encryption | Encrypts only the Password Field | Encrypts the entire payload |
TACACS+ and RADIUS Comparison (Cisco)
Configuring Network Device Management lab solution
REST-Based APIs
REST is acronym for REpresentational State Transfer
Applications use application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate.
API is an interface that defines interactions between multiple software applications or mixed hardware-software intermediaries. A set of functions that allows applications to access data and interact with external software
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/API
REST APIs follow a set of foundational rules about what makes a REST API and what does not. REST APIs include the six attributes defined a few decades Roy Fielding. See https://restfulapi.net.
Those six attributes are
■ Client/server architecture
■ Stateless operation
■ Clear statement of cacheable/uncacheable
■ Uniform interface
■ Layered
■ Code-on-demand
REST APIs and HTTP
The creators of REST-based APIs often choose HTTP because HTTP’s logic matches some of the concepts defined more generally for REST APIs. HTTP uses the same principles as REST: it operates with a client/server model; it uses a stateless operational model; and it includes headers that clearly mark objects as cacheable or not cacheable. It also includes
verbs—words that dictate the desired action for a pair HTTP Request and Reply—which matches how applications like to work.
Routing
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers
SDN
A controller, or SDN controller, centralizes the control of the networking devices. The
degree of control, and the type of control, varies widely.
In a controller-based network architecture, the controller needs to communicate to the networking devices. The 2 APIs interfaces needed are:
- The interface between the controller and those devices, is the southbound interface (SBI).
- A controller’s northbound interface (NBI) opens the controller so its data and functions can
be used by other programs, enabling network programmability, with much quicker development
https://www.baeldung.com/cs/network-traffic-north-south-east-west
SDWAN
The primary components for the Cisco SD-WAN solution consist of the vManage network management system (management plane), the vSmart controller (control plane), the vBond orchestrator (orchestration plane), and the vEdge router (data plane).
- vManage – This centralized network management system provides a GUI interface to easily monitor, configure, and maintain all Cisco SD-WAN devices and links in the underlay and overlay network.
- vSmart controller – This software-based component is responsible for the centralized control plane of the SD-WAN network. It establishes a secure connection to each vEdge router and distributes routes and policy information via the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP), acting as a route reflector. It also orchestrates the secure data plane connectivity between the vEdge routers by distributing crypto key information, allowing for a very scalable, IKE-less architecture.
- vBond orchestrator – This software-based component performs the initial authentication of vEdge devices and orchestrates vSmart and vEdge connectivity. It also has an important role in enabling the communication of devices that sit behind Network Address Translation (NAT).
- vEdge router – This device, available as either a hardware appliance or software-based router, sits at a physical site or in the cloud and provides secure data plane connectivity among the sites over one or more WAN transports. It is responsible for traffic forwarding, security, encryption, Quality of Service (QoS), routing protocols such as Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and more.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/SDWAN/CVD-SD-WAN-Design-2018OCT.pdf
SNMP
How to Configure SNMP Community Strings
https://kb.paessler.com/en/topic/653-how-do-snmp-mibs-and-oids-work
6 SNMP Messages
1. GetRequest
- Function: Retrieves the value of a specific variable (OID) from an SNMP agent.
- Used by: SNMP Manager
- Purpose: To query the status or value of a device attribute, like CPU usage or interface status.
2. GetNextRequest
- Function: Retrieves the value of the next variable in the Management Information Base (MIB) tree.
- Used by: SNMP Manager
- Purpose: Used for iterating through MIB objects, often to walk through a list (e.g., interfaces, routes).
3. GetBulkRequest (SNMPv2 and above)
- Function: Retrieves large blocks of data, such as tables, more efficiently than repeated GetNext requests.
- Used by: SNMP Manager
- Purpose: Reduces overhead by fetching multiple rows of data in one request.
4. SetRequest
- Function: Sets or changes the value of a variable on an SNMP agent.
- Used by: SNMP Manager
- Purpose: To configure device settings, such as enabling/disabling an interface.
5. Response
- Function: Carries the data or acknowledgment from the agent to the manager in reply to Get, Set, or other requests.
- Used by: SNMP Agent
- Purpose: Confirms or denies the success of the manager’s request and returns the requested data.
6. Trap
- Function: An unsolicited message from the agent to the manager indicating a significant event.
- Used by: SNMP Agent
- Purpose: To alert the manager of events like link failures, high CPU usage, or unauthorized access.
The 6 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) messages—also known as Protocol Data Units (PDUs)—are used for network monitoring and management. Here’s a breakdown of each and what they do:
SQL
SSO
A single sign-on (SSO) system allows the user to authenticate once to a local device
and be authorized to access compatible application servers without having to enter
credentials again. For example, a user could log in to a Windows computer using a
Microsoft account and be able to access OneDrive, Teams, Office 365 in Outlook,
and other linked Microsoft and non-Microsoft web services, without having to sign
in again.
One means of implementing SSO is the Kerberos framework. Kerberos provides
SSO authentication to Active Directory, as well as compatibility with other, non-
Windows operating systems. Kerberos was named after the three-headed guard
dog of Hades (Cerberus) because it consists of three parts: Client (which requests
services), Server (from which the service is requested) and a Key Distribution Center
(KDC)—to vouch for their identity.
There are two services that make up a KDC: the Authentication Service and the
Ticket Granting Service.
The Authentication Service is responsible for authenticating user logon requests.
More generally, users and services can be authenticated; these are collectively
referred to as principals. For example, when you sit at a Windows domain
workstation and log on to the domain (Kerberos documentation refers to realms
rather than domains, which is Microsoft’s terminology), the first step of logon is to
authenticate with a KDC server (implemented as a domain controller).
STP ( Spanning Tree Protocol )
Understand and Configure STP on Catalyst Switches
Understanding and Tuning Spanning Tree Protocol Timers
Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2832407&seqNum=5
Rapid Spanning Tree Port States
There are only three port states left in RSTP that correspond to the three possible operational states. The 802.1D disabled, blocking, and listening states are merged into a unique 802.1w discarding state.
| STP (802.1D) Port State | RSTP (802.1w) Port State | Is Port Included in Active Topology? | Is Port Learning MAC Addresses? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disabled | Discarding | No | No |
| Blocking | Discarding | No | No |
| Listening | Discarding | Yes | No |
| Learning | Learning | Yes | Yes |
| Forwarding | Forwarding | Yes | Yes |
Spanning Tree Protocol Operation
https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2832407&seqNum=5
Subnetting
IP Addressing and Subnetting(info on /31 also)
Play the Cisco Binary Game!!!!
https://learningcontent.cisco.com/games/binary/index.html
Switch Virtualization
Cisco StackWise and StackWise Plus Technology
Switch Commands
1. show running-config
- Function: Displays the current active configuration running in the switch’s RAM.
- Use Case: To check the live configuration including interfaces, VLANs, routing, and security settings.
- Example Output: Shows interface settings, passwords (obscured), hostname, and more.
2. show startup-config
- Function: Displays the saved configuration stored in NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM).
- Use Case: To see what configuration will load after the switch is rebooted.
- Tip: Compare this with
show running-configto ensure changes are saved usingcopy running-config startup-config.
3. show interfaces
- Function: Provides detailed statistics about all switch interfaces.
- Use Case: To troubleshoot and monitor interface health, speed, duplex settings, and errors.
- Example Output: Status (up/down), speed, input/output errors, bandwidth usage, etc.
4. show ip interface brief
- Function: Displays a quick summary of all interfaces and their IP addresses and status.
- Use Case: For a fast overview to check if interfaces are up and have IP addresses.
- Example Output: Interface names, IP addresses, status (up/down), and protocol state.
Switch Security ( port security )
Port Security Learning modes
•Static secure MAC addresses: MAC addresses that are manually configured on a port by using the switchport port-security mac-address mac-address interface configuration mode command. MAC addresses configured in this way are stored in the address table and are added to the running configuration on the switch. Use no switchport port-security mac-address mac-address to remove the MAC address if that device is no longer connected to the switch.
•Dynamic secure MAC addresses: MAC addresses that are dynamically learned and stored only in the address table. MAC addresses configured in this way are removed when the switch restarts or when the timer has expired, the optional commands mac address-table aging-time 300 & switchport port-security aging type inactivity will remove the dynamic MAC address after 5 minutes of inactivity.
•Sticky secure MAC addresses: MAC addresses that can be dynamically learned or manually configured are stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration. . Use no switchport port-security mac-address mac-address to remove the MAC address if that device is no longer connected.
Switchport Aging https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1722561
Switch Security Violation modes:
- protect—Drops frames with unknown source addresses until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses to drop below the maximum value.
- restrict—Drops frames with unknown source addresses until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses to drop below the maximum value and causes the SecurityViolation counter to increment and sends SNMP trap notification.
- shutdown—Puts the interface into the error-disabled state immediately and causes the SecurityViolation counter to increment and sends an SNMP trap notification.
Sysloghttps://stackify.com/syslog-101/
Viewing and Managing Log Files (Redhat)
Configuring rsyslog on a Logging Server (Redhat)
https://www.howtoforge.com/how-to-setup-rsyslog-server-on-ubuntu-1804/
TCP
How TCP Three-way handshake works (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK)
Why does TCP even need a 3-way handshake?
TCPDUMP
https://opensource.com/article/18/10/introduction-tcpdump
USERNAMES
Configuring Administrator Usernames and Passwords
VLAN
Creating Ethernet VLANs on Catalyst Switches
Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
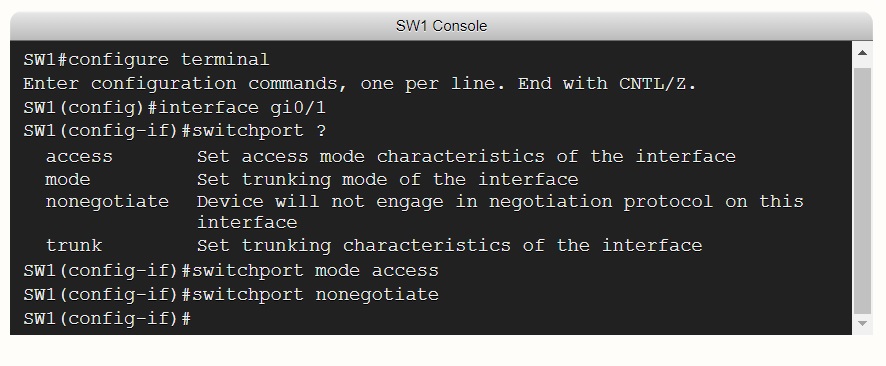
switchport nonegotiate: Prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. You can use this command only when the interface switchport mode is access or trunk. You must manually configure the neighboring interface as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link. Please see the link below Configure DTP for more details.
VXLAN
Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) is a network virtualization technology that attempts to address the scalability problems associated with large cloud computing deployments. It uses a VLAN-like encapsulation technique to encapsulate OSI layer 2 Ethernet frames within layer 4 UDP datagrams, using 4789 as the default IANA-assigned destination UDP port number.[1] VXLAN endpoints, which terminate VXLAN tunnels and may be either virtual or physical switch ports, are known as VXLAN tunnel endpoints (VTEPs).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Extensible_LAN
When an SDA endpoint (for example, an end-user computer) sends a data link frame into an SDA edge node, the ingress edge node encapsulates the frame and sends it across a VXLAN tunnel to the egress edge node
- Fabric edge nodes—SDA nodes that connect to the edge of the SDA fabric—learn the
location of possible endpoints using traditional means, based on their MAC address,
individual IP address, and by subnet, identifying each endpoint with an endpoint identifier (EID). - The fabric edge nodes register the fact that the node can reach a given endpoint (EID)
into a database called the LISP map server. - The LISP map server keeps the list of endpoint identifiers (EIDs) and matching routing
locators (RLOCs) (which identify the fabric edge node that can reach the EID). - In the future, when the fabric data plane needs to forward a message, it will look for and
find the destination in the LISP map server’s database.
Wireshark
Wireshark HTTPS (Has 9 learning Activities.Very good!))
https://wiki.wireshark.org/DisplayFilters
Student Labs
Instructor Token
beevi
Access to Cisco Learning Labs is via the Cisco Learning Labs Portal at the following URL:
https://cll-ng.cisco.com/users/pblogin
Students Credentials
Feedback
Download
Upload
End of David Mark Papkin page on Networking links.
David Papkin favorite movies
Ava Gardner in Singapore (Flim Noir)
Username:
Password: